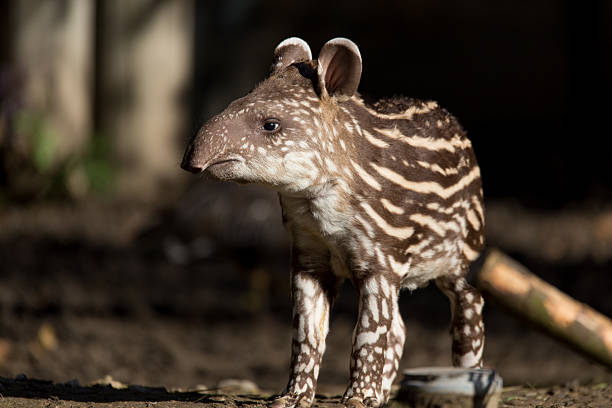
Baird’s Tapir
Baird’s Tapir (Tapirus bairdii)
Baird’s Tapir Facts
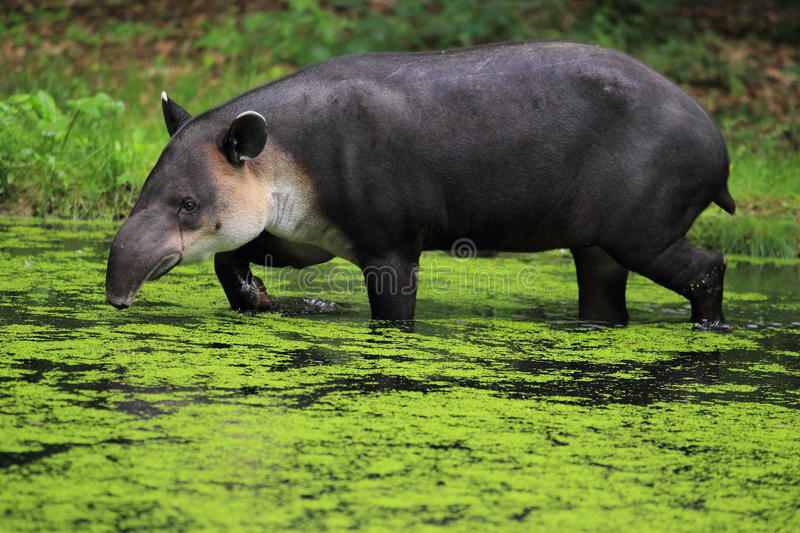
- The Baird’s Tapir is easily identified by its long, fleshy nose, appearing like a shortened elephant’s trunk.
- Its closest relative is the rhinoceros.
- The Baird’s Tapir is the largest indigenous mammal in Central America.
- This elusive Tapir species can live in a wide variety of habitats; tropical forests, lower montane forests, deciduous forests, flooded grasslands and marshes in small regions of Mexico, Central America, and Columbia.
- The Baird’s tapir is a herbivore, that consumes a large amount and variety of vegetation such as leaves, twigs, fruits and seeds as well as aquatic vegetation.
- This shy rarely seen mammal is most active at dusk and throughout the night searching for food. It is sometimes seen in the daytime seeking water to drink and to cool down in the hot weather.
- To communicate, the Baird’s Tapir uses a range of whistles of different pitch and duration.
- The Baird’s Tapir was named after W.M. Baird, an American naturalist who while on a Mexican expedition in 1843 identified the animal.